Introduction
In this YouTube video Kie Codes demonstrated an example of how to generate a melody using a genetic algorithm.
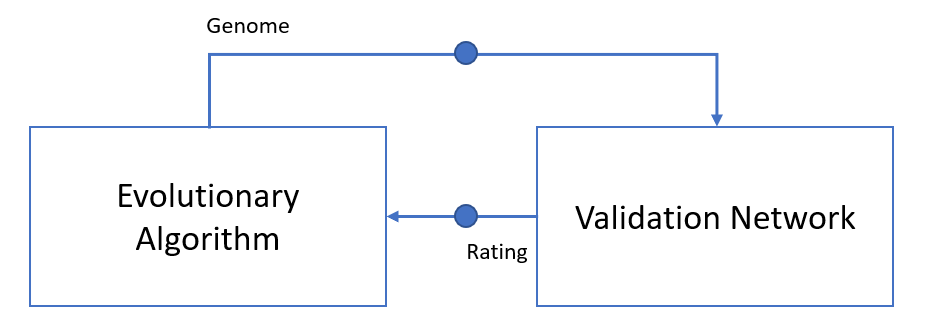
The process involves creating a population of genomes that represent a short melody, and then using an evolutionary algorithm to select the best melodies based on user-provided ratings (on a scale of 0 to 5). The selected melodies are then mated and mutated to generate a new population. The full code for this example can be found on GitHub.
One of the most time-consuming aspects of Kie’s example is the requirement for the user to rate each generated melody by listening to the result. To eliminate this tedious task, we will add an evaluation network that can rate the generated music.
This network will be trained on a subset of labeled melodies to predict the rating of an unseen piece of music. Once the evaluation network is fully trained, the evolutionary algorithm can quickly obtain feedback on the quality of the generated music, without the need for manual rating.
Since the approach with an evaluation network still requires a large amount of labeled data for pre-training, we will implement an active learning mechanism. This means that the network can be pre-trained with a small amount of data, then as it encounters new data, it tracks how certain the model is in its predictions. For the most uncertain melodies, a label is requested from the user, and the model is re-trained based on the new labeled data. This allows for more efficient querying of the user, only when deemed necessary.
By implementing all the components independently (evolutionary algorithm, validation network, and active learner), the waiting time for user input is minimized. The evolutionary algorithm continues to improve while the active learner collects labels and retrains the evaluation network.
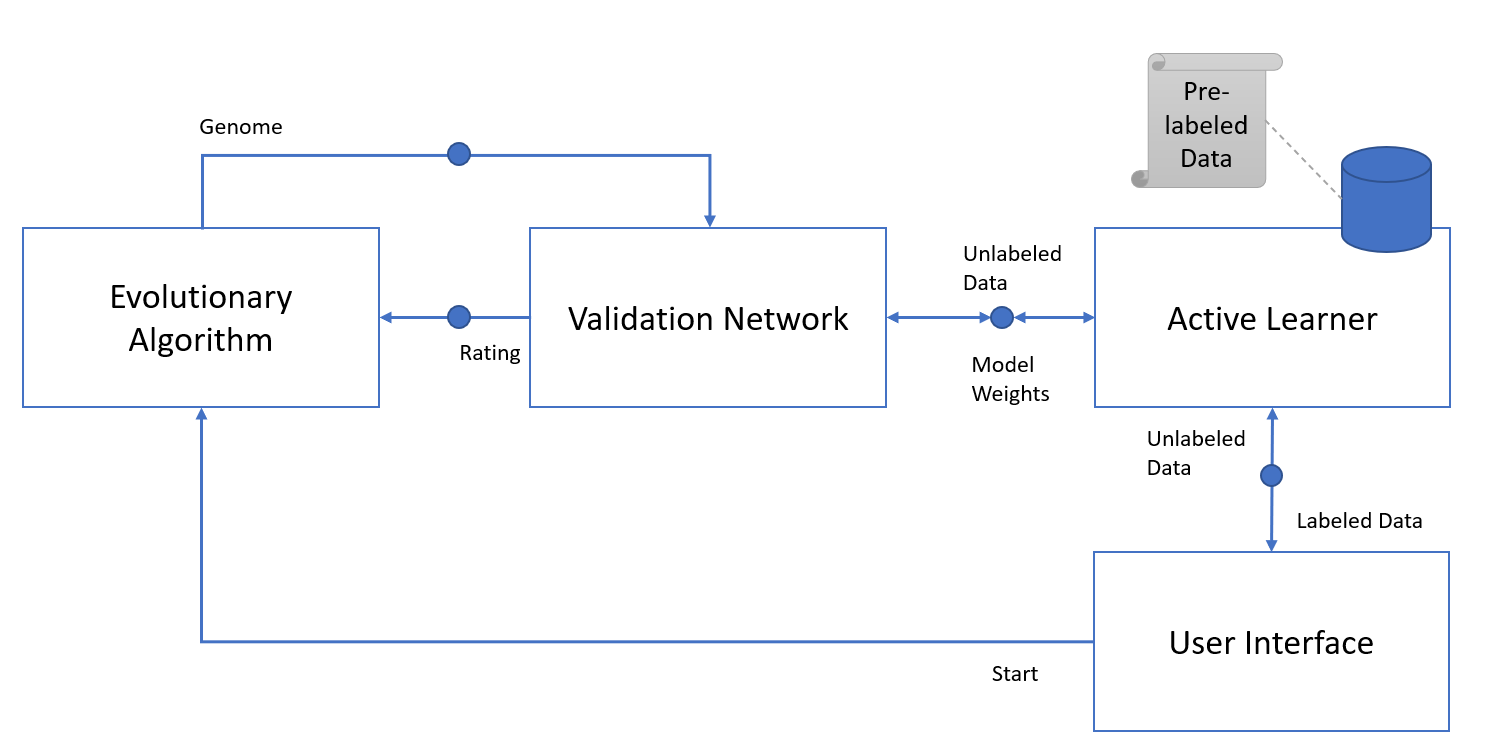
As depicted, we will also include a user interface component to handle the communication for starting and stopping the process, as well as collecting new labels from the user.
This example illustrates how swergio simplifies the process of enabling independent live training across independent components, as well as incorporating user feedback into the loop.
In the following sections, we will examine each component in more detail.